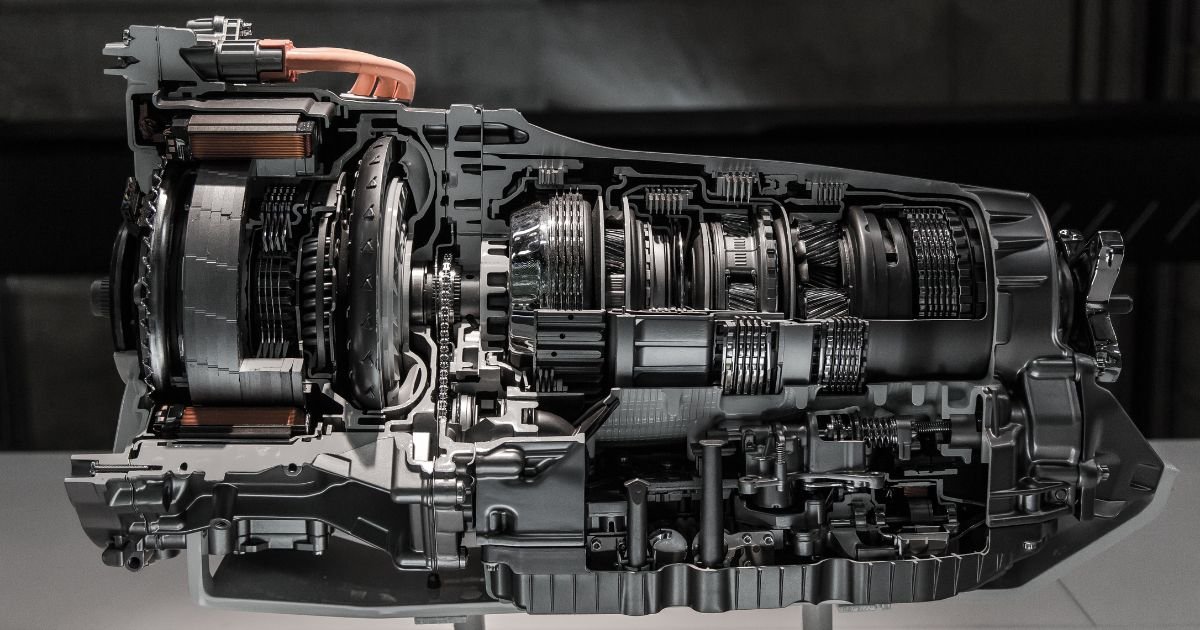
Imagine driving through city traffic without the hassle of constant gear changes. That’s exactly what automatic transmissions do for motor vehicles—they take the stress out of shifting gears while ensuring a smooth and efficient driving experience. Unlike manual transmissions, which require constant driver input, automatic transmissions seamlessly adjust gears using hydraulic systems, torque converters, and planetary gear sets.
But how does this intricate system work? What makes it different from other types of transmissions? And is it really the better choice for all drivers? This complete guide to automatic transmissions breaks down everything you need to know—from the core components to how they operate, their advantages, disadvantages, and different types. Let’s dive in.
What Is Automatic Transmission?
Automatic transmission is a multi-speed transmission system that automatically shifts gears without requiring the driver to operate a clutch. It is a crucial part of modern motor vehicles, enabling a smoother and more effortless driving experience.
Unlike manual transmissions, which rely on direct driver input to change gears, automatic transmissions use a combination of hydraulic automatic mechanisms, electronic controls, and mechanical components to optimize power delivery. This ensures that the engine runs efficiently, providing the right balance between performance and fuel economy.
Automatic transmissions are commonly found in passenger cars, trucks, and SUVs, making driving more accessible to a wider range of people, including beginners and those who prefer convenience over manual shifting.
How Does an Automatic Transmission Work?
The functioning of an automatic transmission revolves around fluid dynamics, torque transfer, and gear shifting mechanisms. Instead of a clutch, automatic transmissions use a torque converter, a fluid coupling that connects the engine to the transmission. Here’s a step-by-step look at how it operates:
- Torque Converter Activation: The engine’s power is transferred to the transmission via a torque converter, which consists of a pump (impeller), turbine, stator (reactor), and a torque converter clutch. These components work together to control the flow of transmission fluid, allowing the vehicle to accelerate smoothly.
- Hydraulic Pressure and Gear Shifting: The transmission uses pressurized hydraulic fluid to engage various planetary gears, which determine the appropriate gear ratio based on speed and load.
- Brake Bands and Clutches: These elements help lock or unlock different gears, enabling a seamless transition between speeds.
- Electronic Controls: Modern automatic transmissions incorporate electronic sensors that adjust shifting patterns based on real-time driving conditions, ensuring efficiency and fuel savings.
Parts of an Automatic Transmission
An automatic transmission is a complex mechanical system with several essential components working in harmony. Let’s break down its main parts:
1. Transmission Casing
The transmission casing houses all the internal components, protecting them from external damage while keeping the lubricating fluid contained.
2. Torque Converter
Instead of a traditional clutch, automatic transmissions use a torque converter to connect the engine to the transmission. It controls the transfer of power by adjusting hydraulic pressure.
3. Pump (aka Impeller)
The pump, also called the impeller, circulates transmission fluid within the torque converter, enabling smooth power transfer.
4. Turbine
The turbine receives energy from the fluid movement inside the torque converter and transmits it to the transmission system.
5. Stator (aka Reactor)
The stator redirects fluid flow within the torque converter, improving efficiency and torque multiplication.
6. Torque Converter Clutch
In some systems, a torque converter clutch locks the converter at higher speeds, improving fuel economy by reducing power loss.
7. Planetary Gear System
The planetary gear system is the core mechanism that provides different gear ratios, allowing the vehicle to accelerate or decelerate smoothly.
8. Brake Bands and Clutches
These components engage and disengage different gears in the planetary system, ensuring proper gear selection based on driving conditions.
What Are the Types of Automatic Transmission?
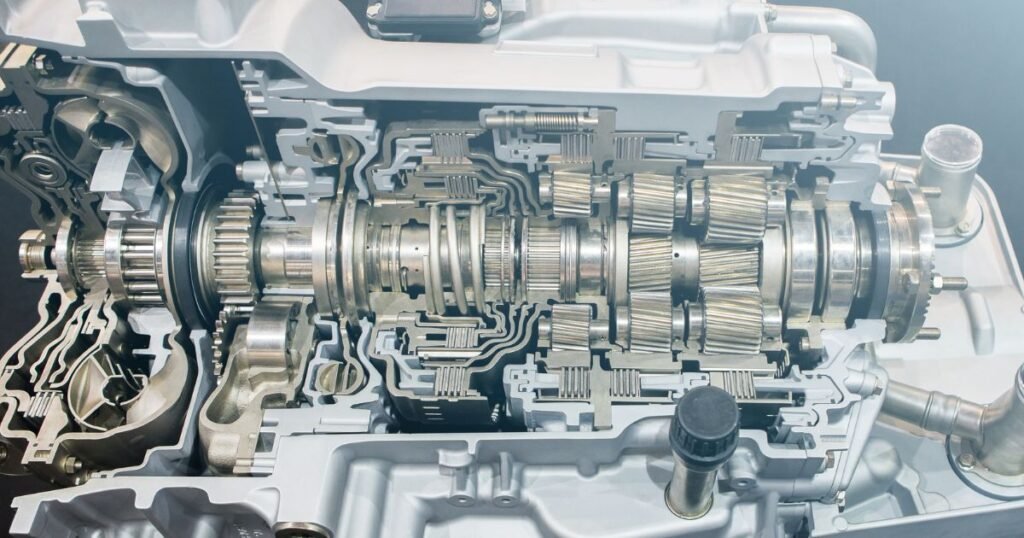

Automatic transmissions come in various types, each designed for different driving needs and vehicle applications. Below are the four main types:
1. Automated Manual Transmission (AMT)
AMTs use a conventional manual transmission but automate the clutch and gear-shifting process using sensors and actuators. This offers the benefits of an automatic transmission while retaining the fuel efficiency of a manual gearbox.
2. Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
Unlike traditional multi-speed transmissions, a CVT uses a belt and pulley system to provide an infinite number of gear ratios. This results in seamless acceleration without distinct gear shifts, improving fuel efficiency.
3. Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT)
A DCT utilizes two separate clutches—one for even gears and one for odd gears—to enable lightning-fast gear shifts. It offers the efficiency of a manual transmission with the convenience of an automatic.
4. Fully-Automatic Transmission
The most common type, fully-automatic transmissions, rely entirely on hydraulic and electronic systems to manage gear shifts. They are the easiest to drive and are widely used in passenger cars.
Advantages of Automatic Transmission
Automatic transmissions offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice for many drivers:
- Convenience: Eliminates the need for manual gear shifting, making driving effortless, especially in heavy traffic.
- Smooth Performance: Gear shifts are seamless, reducing jerky movements and improving ride comfort.
- Easier to Learn: Ideal for beginner drivers since there’s no clutch operation involved.
- Less Driver Fatigue: Long drives are more comfortable as drivers don’t need to worry about constant gear changes.
- Advanced Safety Features: Many modern automatic transmissions integrate with safety systems like adaptive cruise control.
Disadvantages of Automatic Transmission
While automatic transmissions provide convenience, they come with certain drawbacks:
- Higher Cost: Automatic transmissions are generally more expensive than manual counterparts in both purchase price and repairs.
- Lower Fuel Efficiency (in Some Cases): Some older automatic transmissions consume more fuel compared to manuals.
- Complex Maintenance: Repairs and replacements can be costly due to their intricate design.
- Reduced Engine Control: Enthusiasts prefer manual transmissions as they offer better control over acceleration and deceleration.
- Heavier Weight: Automatic systems add extra weight to a vehicle, which can slightly impact performance.
Is an Automatic Transmission Better Than a Manual Transmission?
Deciding between an automatic and manual transmission depends on your driving preferences and needs. Automatic transmissions are better suited for urban commuting and effortless driving, while manual transmissions provide better control and fuel efficiency for enthusiasts who enjoy an engaging driving experience.
For drivers who prioritize ease and comfort, automatic transmissions are the clear winner. However, those looking for performance and cost savings may still prefer manual transmissions.
How to Maintain an Automatic Transmission for Longevity?
Maintaining an automatic transmission is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and extending its lifespan. Since automatic transmissions rely on hydraulic fluid and complex internal components, neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs. Follow these essential maintenance tips to keep your transmission in optimal condition:
1. Regular Transmission Fluid Checks and Changes
Transmission fluid serves as a lubricant, coolant, and hydraulic medium. Over time, it degrades and loses its effectiveness, leading to poor performance and overheating. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended intervals for fluid changes.
- Check the fluid level and color regularly. Fresh fluid is typically red and transparent, while dark or burnt-smelling fluid indicates contamination.
- Use the correct type of transmission fluid recommended for your vehicle.
- Ensure that there are no leaks, as low fluid levels can cause transmission failure.
2. Avoid Aggressive Driving
Sudden acceleration, hard braking, and rapid gear shifts put excessive strain on the transmission system. Driving smoothly helps reduce wear and tear on planetary gears, brake bands, and clutches.
3. Allow the Transmission to Warm Up
In cold weather, let the engine idle for a minute before driving. This allows the transmission fluid to circulate properly, ensuring that all components are lubricated and function smoothly.
4. Inspect the Transmission Cooling System
Automatic transmissions generate heat, and overheating is one of the leading causes of transmission failure. Ensure the cooling system, including the radiator and transmission cooler, is functioning correctly to prevent damage.
5. Get Routine Transmission Inspections
Periodic transmission checkups by a qualified mechanic can help detect potential issues before they become serious problems. This includes checking electronic sensors, valve bodies, and solenoids for proper operation.
Common Automatic Transmission Problems and Their Solutions
Automatic transmissions are built for durability, but issues can still arise over time. Below are some common transmission problems and their solutions:
1. Slipping Gears
If your transmission randomly shifts gears or struggles to stay in gear, it might be due to low transmission fluid, worn-out clutches, or damaged planetary gears.
Solution: Check and refill the transmission fluid. If the problem persists, a transmission inspection is necessary to identify worn components.
2. Delayed or Rough Shifting
A noticeable delay when shifting gears or a jerky transition may indicate issues with transmission bands, solenoids, or fluid contamination.
Solution: Perform a transmission fluid change. If the issue continues, have a technician inspect the valve body and hydraulic system.
3. Overheating Transmission
Excessive heat is a leading cause of transmission failure. It occurs due to low fluid levels, heavy towing, or malfunctioning coolers.
Solution: Check the cooling system and ensure the radiator is functioning. Adding an auxiliary transmission cooler can help prevent overheating.
4. Strange Noises (Whining, Grinding, or Clunking)
Unusual noises while driving can indicate bearing wear, fluid starvation, or damaged gears.
Solution: If noises persist, get a professional diagnosis. Ignoring strange sounds can lead to severe internal transmission damage.
5. Check Engine Light is On
Modern vehicles have sensors that monitor transmission performance. If the check engine light is illuminated, the transmission may have sensor malfunctions or slipping issues.
Solution: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for error codes. Transmission-related codes should be addressed by a professional mechanic.
Automatic Transmission vs. Manual Transmission: Which One is Right for You?
Choosing between an automatic and manual transmission depends on various factors such as driving habits, cost considerations, and performance preferences. Let’s compare them:
1. Ease of Use
- Automatic: Requires minimal driver effort—just shift into “Drive” and go.
- Manual: Requires the driver to manually change gears using a clutch.
Winner: Automatic transmissions offer better convenience, especially in stop-and-go traffic.
2. Fuel Efficiency
- Manual: Traditionally more fuel-efficient, but modern automatic transmissions (CVTs, DCTs) have closed the gap.
- Automatic: Older models consume more fuel, but newer fully-automatic transmissions are optimized for efficiency.
Winner: Depends on the vehicle. Some modern automatics are just as efficient as manuals.
3. Maintenance and Repair Costs
- Automatic: Higher maintenance and repair costs due to complex internal components.
- Manual: Cheaper repairs, as clutch replacements are more affordable than full automatic rebuilds.
Winner: Manual transmissions are cheaper to maintain.
4. Driving Experience
- Automatic: Smooth and stress-free, especially for daily commuting.
- Manual: Provides better control, making it a favorite among car enthusiasts.
Winner: Depends on personal preference. Enthusiasts prefer manual, while everyday drivers enjoy the convenience of automatics.
5. Longevity and Durability
- Manual: Generally lasts longer since it has fewer electronic components.
- Automatic: More prone to wear and tear, requiring regular maintenance.
Winner: Manual transmissions are typically more durable.
Future of Automatic Transmissions: What’s Next?
With rapid advancements in automotive technology, automatic transmissions are evolving to become more efficient, durable, and responsive. The future holds promising innovations:
1. AI-Driven Transmission Systems
Modern vehicles are integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to optimize shifting patterns, improving both performance and fuel economy.
2. Fully Autonomous Transmission Technology
As self-driving cars gain traction, transmission systems will adapt to work seamlessly with autonomous control systems, eliminating the need for driver input entirely.
3. Improved CVT and Dual-Clutch Transmissions
Automakers are refining CVT and DCT technology to reduce lag and enhance smoothness. Future CVTs may incorporate electric motors for enhanced hybrid performance.
4. Electric Vehicle (EV) Transmissions
Most electric cars don’t require multi-speed transmissions, but some manufacturers are exploring two-speed automatic transmissions for increased energy efficiency and acceleration.
Conclusion
Automatic transmissions have revolutionized the driving experience, offering ease, comfort, and improved efficiency. Whether you drive a traditional fully-automatic, CVT, AMT, or DCT, understanding how these systems work and maintaining them properly ensures a smoother, longer-lasting driving experience.
With continuous technological advancements, the future of automatic transmissions promises smarter, more efficient, and more durable designs. Whether you’re a daily commuter, a performance enthusiast, or considering an electric vehicle, the evolution of automatic transmissions will continue to enhance driving experiences for years to come.
FAQs
Does an automatic transmission use more fuel than a manual transmission?
Traditionally, manual transmissions were more fuel-efficient, but modern automatic transmissions, especially CVTs and DCTs, have significantly improved efficiency, making the difference negligible.
How long does an automatic transmission last?
With proper maintenance, an automatic transmission can last 100,000 to 200,000 miles. Regular fluid changes and avoiding aggressive driving can extend its lifespan.
Can I switch from automatic to manual mode in an automatic transmission?
Yes, many modern vehicles feature a manual mode (also called Tiptronic or paddle-shift systems) that allows drivers to control gear changes manually while retaining the convenience of an automatic.