When you look at your car, you’re actually looking at dozens of carefully designed components working together to create a functional, safe, and aesthetically pleasing vehicle. Understanding car body parts names isn’t just for mechanics or automotive enthusiasts—it’s practical knowledge that can help every car owner communicate issues effectively, make informed purchasing decisions, and appreciate the engineering marvel that is the modern automobile.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore over 40 car body parts names, their functions, locations, and importance in the overall vehicle structure. Whether you’re dealing with a minor repair, shopping for a new vehicle, or simply expanding your automotive knowledge, this guide to car body parts will serve as your roadmap to understanding the exterior and interior components that make up your automobile’s body.
How many body parts does a car have?
A typical passenger car consists of approximately 30,000 parts in total, with the body structure alone comprising over 40 major components. From prominent exterior elements like the hood and doors to less visible but crucial components like fender liners and radiator supports, each part serves a specific purpose in the vehicle’s functionality, safety, and aesthetics.
Why is it important to know car body parts names?
Knowledge of car body parts names empowers you in several ways:
- Effective communication: When describing damage or required repairs to mechanics or insurance adjusters, precise terminology ensures clarity.
- Informed purchasing: Whether buying a new vehicle or replacement parts, understanding the components helps you make better decisions.
- DIY maintenance: Many minor repairs and maintenance tasks can be handled independently with proper knowledge of vehicle body components.
- Safety awareness: Understanding how body parts contribute to your car’s safety systems helps you appreciate proper maintenance and prompt repairs.
What are the names of car body parts?
Here’s a comprehensive list of the main car body parts you should be familiar with:
- Body shell
- Hood or bonnet
- Front bumper
- Rear bumper
- Bumper grille
- Crash guard or bullbar
- Wiper blade
- Headlight
- Fog lamp
- Indicator lights
- Cowl panel
- Quarter panel
- Fender
- Fender liners
- Radiator
- Radiator supports.
- Mirrors
- Doors
- Door handle
- Window glass
- Roof
- Sunroof
- Trunk or decklids
- Quarter window
- Wheels
- Mud flaps
- Hubcap
- Dashboard
- Taillights
- Number plate
1. Body shell
The body shell, also called the unibody or monocoque, forms the main structural foundation of the vehicle. This rigid metal framework integrates the floor pan, roof, pillars, and side panels into a single structural unit. In modern cars, the body shell is designed for optimal crash protection while minimizing weight. Unlike older vehicles with separate chassis frames, most modern automobiles use this integrated design approach for better handling, fuel efficiency, and safety.
2. Hood or bonnet
The hood (or bonnet in British English) is the hinged cover that provides access to the engine compartment at the front of the car. This large, movable panel is typically made of lightweight materials like aluminum or composite materials to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity. The car’s bonnet often features reinforcement structures underneath to enhance crash protection and may include safety latches to prevent it from flying open while driving.
3. Front bumper
The front bumper is the protective barrier at the vehicle’s front end, designed to absorb impact energy in low-speed collisions. Modern car front parts include not just the visible bumper cover, but also energy-absorbing foam, impact bars, and mounting brackets beneath the cosmetic exterior. The front bumper often houses fog lamps, air intakes, and sensors for driver assistance systems, making it more than just a protective element but an integral part of the car’s front-end design and functionality.
4. Rear bumper
Similar to the front bumper, the rear bumper protects the back of the automobile from low-impact collisions. This component includes the visible bumper cover and underlying reinforcement structures. In many modern vehicles, the rear bumper integrates parking sensors, exhaust outlets, and reflectors. The design of rear bumper parts varies significantly across different vehicle models, balancing aesthetic appeal with functional protection.
5. Bumper grille
The bumper grille is an opening in the front bumper that allows airflow to critical components like the radiator and intercooler. This mesh or slotted design element serves both functional and aesthetic purposes. In many high-performance vehicles, these grilles direct cooling air precisely where needed, while in luxury cars, they often feature distinctive styling that helps define the brand’s identity.
6. Crash guard or bullbar
The crash guard (also called a bullbar or push bar) provides additional front-end protection on SUVs, trucks, and off-road vehicles. These robust metal structures mount to the vehicle’s frame and shield the front of a car from damage during off-road driving or animal strikes. While enhancing protection, these components must be carefully designed not to interfere with the car’s engineered crumple zones and airbag systems.
7. Headlight
Headlights are crucial illumination systems that make night driving possible. Modern headlight assemblies are complex units containing multiple bulbs or LED arrays, reflectors, lenses, and sometimes motors for adaptive lighting. Beyond basic illumination, current automotive lighting systems may include daytime running lights, cornering lights, and high-beam assist features that automatically adjust to traffic conditions.
8. Fog lamp
Mounted low on the front bumper, fog lamps provide illumination during conditions of reduced visibility. These specialized lights produce a wide, flat beam that minimizes reflection off fog, snow, or rain. Unlike regular headlights that can cause glare in foggy conditions, these focused light sources help drivers see the road surface and edges more clearly in adverse weather.
9. Indicator lights
Also known as turn signals or blinkers, indicator lights communicate the driver’s intentions to turn or change lanes. Modern vehicles feature these amber-colored lights at the front, sides, and rear of the vehicle body. Some luxury cars incorporate dynamic or sequential indicator patterns for enhanced visibility and style. These simple but essential communication devices help prevent accidents by making driver intentions clear to other road users.
10. Wiper blade
While the wiper blades themselves are replaceable rubber components, they connect to wiper arms that are mounted to the cowl area of the car body. This system clears the windshield of rain, snow, and debris to maintain visibility. Many modern cars also feature rear wipers and sophisticated systems that adjust wiper speed automatically based on rainfall intensity.
11. Radiator
Although technically an engine component, the radiator mounts to the front body structure of the car. This heat exchanger cools the engine coolant by transferring heat to the air flowing through its fins. The positioning of the radiator behind the front grille allows for optimal airflow while driving, making it an essential component whose placement is carefully integrated with the vehicle’s front-end design.
12. Radiator supports
These structural members secure the radiator and often other front-end components like the AC condenser and cooling fans to the vehicle body. Radiator supports provide rigid mounting points while allowing for some flexibility to absorb minor impacts. These components must balance strength with appropriate crash deformation characteristics to protect both the cooling system and passengers.
13. Cowl panel
The cowl panel is the structural element that connects the windshield to the hood area. This often-overlooked car body part seals the gap between the hood and windshield, prevents water intrusion into the cabin, and houses the wiper system mounting points. It represents an important transition point between the engine compartment and passenger cabin in the vehicle’s structure.
14. Quarter panel
The quarter panels are the side body sections between the rear doors and the trunk area. These large sheet metal sections form the rear fenders and integrate with the vehicle’s overall side profile. In modern unibody construction, quarter panels are typically welded into the body structure and require significant work to replace if damaged, making them among the more complex car body components to repair.
15. Fender
Fenders are the body panels that surround and protect the wheel wells. Front fenders extend from the front doors to the front bumper, while rear fenders (often integrated into the quarter panels) surround the rear wheels. Unlike a car bumper, which absorbs impact, a car fender primarily protects against debris thrown by the wheels and contributes to the vehicle’s aerodynamic profile.
16. Fender liners
Made of plastic or rubber, fender liners protect the inside of the fender wells from water, dirt, and road debris. These protective shields help prevent corrosion and premature wear of suspension and body components. While not visible from the exterior, these practical components significantly extend the life of many vehicle systems by creating a barrier between road elements and sensitive mechanical parts.
17. Roof
The roof panel forms the upper covering of the passenger compartment. In modern cars, this structural element contributes significantly to the overall rigidity of the vehicle body. Automobile manufacturers increasingly offer options like panoramic sunroofs, removable roof panels, or convertible tops that transform this fundamental structural element into a lifestyle feature.
18. Sunroof
A sunroof is a movable panel in the roof that can be opened to allow light and air into the cabin. Modern vehicles offer various sunroof designs, from simple tilting panels to complex panoramic systems that span nearly the entire roof area. This desirable feature requires precise integration with the roof structure to maintain structural integrity while providing the open-air experience many drivers enjoy.
19. Mirrors
Side-view mirrors (or wing mirrors) mount to the front doors or A-pillars and provide visibility to the sides and rear of the vehicle. Modern car mirrors often include integrated turn signals, heating elements, power adjustment, auto-dimming features, and even cameras for blind-spot monitoring systems. The housing and mounting points for these essential visibility tools are carefully designed as part of the overall vehicle body structure.
20. Doors
Car doors are complex assemblies that include the outer skin, inner panel, intrusion beams, window regulators, and locking mechanisms. Vehicle doors must balance ease of use with structural strength for side-impact protection. Modern car door parts often integrate advanced features like acoustic insulation, water-deflection channels, and precisely engineered hinges and latches for optimal feel and function.
21. Door handle
Door handles provide the mechanical interface for opening the vehicle doors. Contemporary designs range from traditional pull handles to flush-mounted electronic touchpoints in luxury and electric vehicles. These seemingly simple car body components require careful engineering to function reliably through thousands of cycles while maintaining security and safety during a collision.
22. Window glass
Automotive glass includes the windshield, side windows, and rear window. Modern car windows are typically made of laminated safety glass for the windshield and tempered glass for the sides and rear. These transparent components are structurally integral to the vehicle, contributing to rigidity while providing visibility and protection from the elements. Advanced glass technologies now include acoustic damping, UV filtering, and even electrochromic darkening features.
23. Quarter window
Quarter windows are the small fixed or movable glass panels usually located at the rear sides of the vehicle. These small windows improve visibility around the C-pillars and enhance the overall greenhouse design. In some vehicles, these windows are engineered to open for additional ventilation, while in others they remain fixed as part of the overall body structure.
24. Trunk or decklids
The trunk (or boot in British English) is the covered cargo area at the vehicle’s rear. This large hinged panel provides access to the luggage compartment in sedans and coupes. In hatchback designs, this component is larger and includes the rear window. Modern trunk lids often integrate aerodynamic spoilers, third brake lights, and, in some cases, complex multi-link opening mechanisms for easier access.
25. Mud flaps
Mud flaps are protective panels installed behind the wheels to prevent water, mud, and debris from being thrown against the vehicle body or other vehicles. While sometimes considered accessories, many vehicles integrate these protective elements directly into the fender design. These practical additions help protect the vehicle finish and improve visibility for following drivers in wet conditions.
26. Wheels
While primarily mechanical components, wheels are increasingly designed as integral aesthetic elements of the vehicle body. Modern alloy wheels balance structural requirements with aerodynamic efficiency and visual appeal. The visual integration of wheels with body styling has become an important aspect of automotive design, with wheel arches and fenders specifically shaped to complement wheel designs.
27. Hubcap
Hubcaps are decorative covers that conceal the center portion of the wheel. While less common on modern vehicles with alloy wheels, hubcaps remain important on base-model cars with steel wheels. These components protect the wheel hub and lug nuts while improving aerodynamics and providing a more finished appearance to the vehicle’s side profile.
28. Dashboard
The dashboard (or instrument panel) forms the main interior interface between the driver and the vehicle. This complex assembly houses instruments, controls, air vents, airbags, and, increasingly, digital displays. While technically an interior component, the dashboard mounts directly to the vehicle body structure and serves as a critical element in both the driving experience and passenger safety systems.
29. Number plate
License plate mounting areas are specific regions of the front and rear body panels designed to accommodate legally required registration plates. These seemingly simple areas require careful integration with bumper covers, trunk lids, or front fascias, often including lighting for nighttime visibility as required by law in many jurisdictions.
30. Taillights
Taillights are the red lights at the rear of the vehicle that illuminate when braking or during nighttime driving. Modern taillight assemblies are sophisticated components incorporating brake lights, turn signals, reverse lights, and sometimes fog lamps in a single integrated unit. Contemporary designs often use LED technology to create distinctive lighting signatures that enhance brand identity while improving visibility and safety.
What are the different car door parts and their functions?
The car door is a sophisticated assembly consisting of several interconnected components:
- Door skin: The visible outer metal or composite panel
- Door frame: The structural skeleton that supports all components
- Window regulator: The mechanism that raises and lowers the window
- Door lock actuator: Controls the locking mechanism electrically
- Interior door panel: The finished inner surface with controls and armrests
- Door hinges: Connect the door to the vehicle body and allow it to swing open
- Intrusion beam: A reinforced bar that provides side-impact protection
Each of these car door parts contributes to convenience, safety, and the overall structural integrity of the vehicle body.
What are the names of exterior car body parts?
Exterior car body parts include:
- Hood/bonnet
- Fenders
- Doors
- Roof
- Quarter panels
- Trunk/boot lid
- Bumpers (front and rear)
- Grille
- Headlights and taillights
- Side mirrors
- Pillars (A, B, C, and sometimes D)
- Window frames
- Fuel door
- Wheel arches
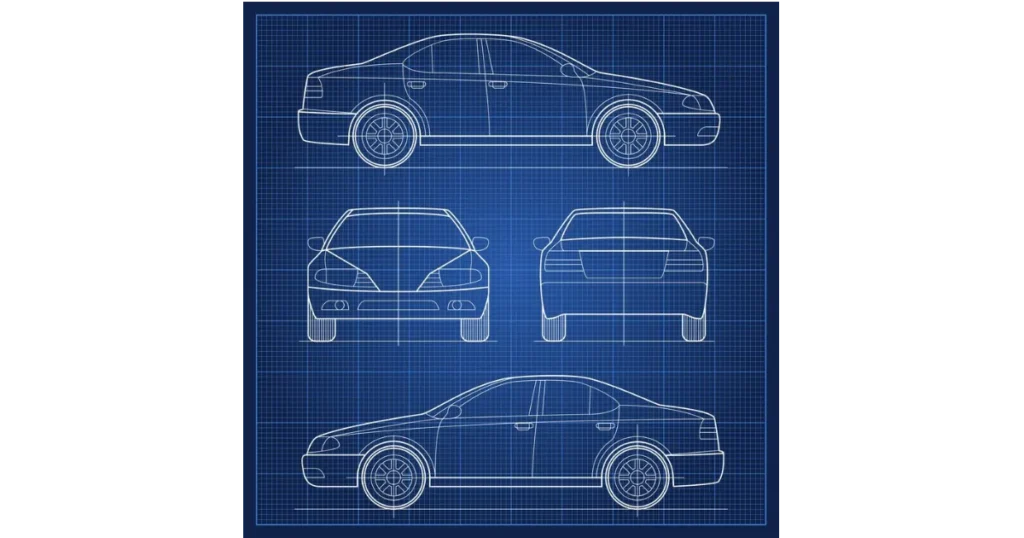
These visible automobile body components define the vehicle’s appearance while providing protection, aerodynamics, and structural integrity.
What are the names of Interior car body parts?
Interior car body components include:
- Dashboard/instrument panel
- Center console
- Door panels
- Headliner
- Pillars (interior covering)
- Seat frames
- Cargo area/trunk interior
- Kick panels
- Floor pan
- Firewall
- Package tray
These interior structural and trim elements create the passenger cabin space while contributing to comfort, safety, and noise reduction.
What are the names of car body parts on the front side?
The front of the vehicle includes these essential car front parts:
- Front bumper cover
- Grille
- Hood/bonnet
- Front fenders
- Headlights
- Fog lights
- Front windshield
- Front bumper reinforcement
- Radiator support
- Front license plate mount
- Hood latch and release mechanism
These front parts of a car components work together to create the vehicle’s distinctive face while protecting critical mechanical systems.
What are the names of car body parts on the back side?
The rear part of a car includes:
- Rear bumper cover
- Trunk lid/hatch/tailgate
- Taillights
- Rear window/glass
- Rear quarter panels
- Rear license plate area
- Exhaust tips
- Rear reflectors
- Rear spoiler (if equipped)
- Rear wiper (on hatchbacks and SUVs)
These rear car body parts define the vehicle’s back profile while integrating storage access and essential lighting.
What are the names of side car body parts?
The side profile of a vehicle includes:
- Doors
- Side mirrors
- Fenders
- Quarter panels
- Rocker panels
- Side skirts
- Pillars (A, B, C, and sometimes D)
- Side windows
- Wheel arches
- Fuel door
- Side marker lights
These components create the vehicle’s side silhouette while providing structural integrity and access to the interior.

What is a car bonnet?
The car’s bonnet, known as the hood in American English, is the hinged cover that provides access to the engine compartment at the front of the vehicle. This large metal or composite panel serves multiple purposes:
- It protects the engine and other components from weather and debris
- It contributes to the vehicle’s aerodynamic efficiency
- It absorbs energy in frontal crashes through designed crumple zones
- It enhances the overall aesthetic design of the automobile
Modern bonnets typically feature a double-layer construction with reinforcement ridges for structural integrity while minimizing weight. They connect to the vehicle body via hinges at the rear edge and are secured by a latch system at the front.
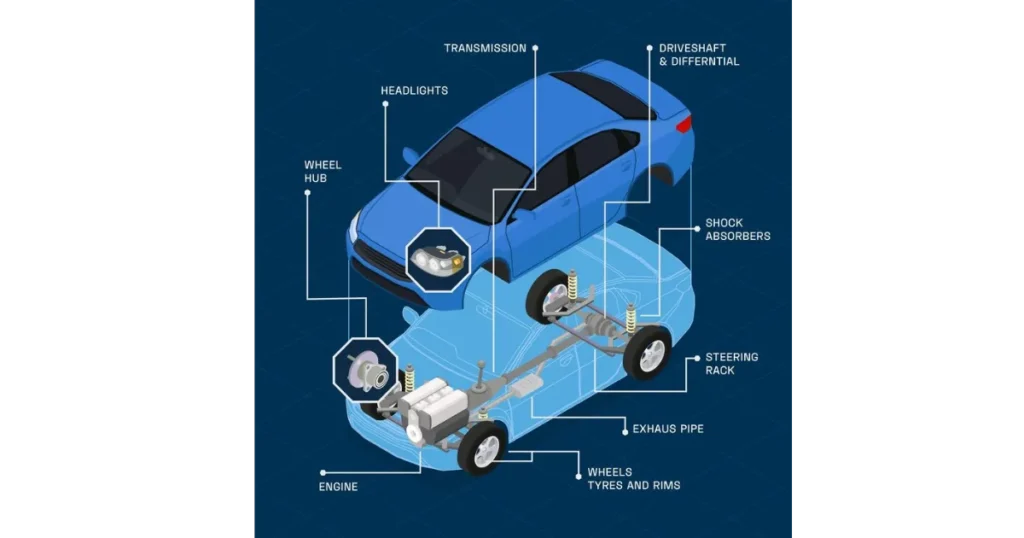
What are the parts located under the bonnet of a car?
When you open the bonnet, you’ll find several critical components:
- Engine block: The core of the power system
- Battery: Provides electrical power for starting and accessories
- Radiator: Cools the engine by dissipating heat
- Air filter housing: Contains the filter that cleans incoming air
- Fluid reservoirs: For brake fluid, power steering fluid, coolant, and windshield washer fluid
- Fuse box: Houses electrical fuses and relays
- Strut towers: Structural mounting points for the suspension
- Hood latch mechanism: The receiving end of the hood’s locking system
- Sound insulation: Padding that reduces engine noise
While these are primarily mechanical rather than body components, they’re all accessed through the bonnet opening and many mount directly to the body structure.
What is the difference between a car fender and a bumper?
Though often confused, fenders and bumpers serve distinct purposes in the vehicle body structure:
Fender:
- Located around the wheel wells
- The primary purpose is to contain debris thrown by the wheels
- Forms part of the vehicle’s side profile
- Typically made of sheet metal or composite materials
- Integrated into the overall body structure
- Designed primarily for appearance and aerodynamics
Bumper:
- Located at the extreme front and rear of the vehicle
- The primary purpose is to absorb impact energy in low-speed collisions
- Consists of a visible cover plus internal reinforcement and energy-absorbing materials
- Made of flexible plastics over a rigid structure
- Mounted to the vehicle frame or unibody
- Designed primarily for safety and damage prevention
Understanding this fender vs bumper distinction helps when communicating about vehicle damage or repairs.
What are the names of the rear bumper parts?
The rear bumper assembly includes:
- Bumper cover (the visible plastic or painted exterior)
- Impact absorber (foam or honeycomb structure)
- Bumper reinforcement bar (metal structural component)
- Bumper mounting brackets
- Reflectors
- Parking sensor housings (in equipped vehicles)
- Exhaust cutouts
- Step pad (in SUVs and trucks)
- License plate mounting area
- Trailer hitch cover (if applicable)
These components work together to provide protection while integrating with the vehicle’s rear styling.
What materials are used for car body parts?
Modern vehicle body components utilize a variety of materials:
- Steel: Traditional material used for structural elements; newer high-strength and ultra-high-strength steels reduce weight while maintaining rigidity
- Aluminum: Increasingly common for hoods, doors, and entire body structures to reduce weight
- Carbon fiber: Premium lightweight material used in high-performance vehicles
- Fiberglass: Used for specialized applications and some replacement parts
- Plastic/polymer composites: Common for bumper covers, interior trim, and non-structural exterior elements
- Magnesium: Ultra-lightweight metal used for specific structural components
- Glass: Used for windows and increasingly for panoramic roofs
Manufacturers strategically select materials to balance strength, weight, cost, and manufacturability across the vehicle body.
What is the function of the chassis in a vehicle?
The chassis forms the underlying framework to which all other components attach. In body-on-frame vehicles (typically trucks and some SUVs), the chassis is a separate structure from the body. In unibody construction (most modern passenger cars), the chassis and body shell are integrated into a single unit.
Key functions of the chassis include:
- Providing structural support for all vehicle systems
- Absorbing and distributing road forces
- Creating mounting points for suspension, drivetrain, and body
- Contributing to crash protection through controlled deformation
- Minimizing vibration and harshness
The chassis design significantly influences the vehicle’s handling characteristics, ride quality, and overall durability.
How does the frame support the overall body structure?
In modern unibody vehicles, the frame elements are integrated into the body shell through a combination of:
- Longitudinal rails: Run front-to-back, providing the main structural spine
- Cross-members: Connect the rails laterally for torsional rigidity
- Crumple zones: Engineered sections designed to absorb impact energy
- Reinforced safety cage: Surrounds the passenger compartment
- Suspension mounting points: High-strength areas that handle dynamic loads
- Engine cradle: Subframe that supports the powertrain
This integrated approach creates a lightweight yet rigid structure that balances handling performance with passenger protection.
FAQ’s About Car Body Parts Names
Can you provide a list of automobile parts names?
Major automobile body parts include:
- Body shell/unibody
- Hood/bonnet
- Trunk/boot/hatch
- Fenders
- Doors
- Roof
- Bumpers
- Grille
- Quarter panels
- Pillars (A, B, C)
- Mirrors
- Windows
- Lights (head, tail, fog, indicators)
This list covers the primary external components that make up a vehicle’s body structure.
What are the side body panels of a car called?
The side body panels include:
- Front fenders
- Doors
- Quarter panels
- Rocker panels (also called sills)
- Side skirts (decorative additions)
These components create the vehicle’s side profile while providing structural integrity and protection.
What is the roof of a car called?
The roof panel forms the upper covering of the passenger compartment. Variations include:
- Hardtop: Standard fixed roof
- Sunroof/moonroof: With opening panel
- Panoramic roof: Extended glass sections
- Convertible top: Fully retractable
- T-top: With removable panels
- Targa top: With central removable section
The roof contributes significantly to the vehicle’s structural rigidity and rollover protection.
What is the rear part of a car called?
The rear section includes multiple components:
- Trunk/boot lid or hatch
- Rear bumper
- Taillights
- Rear quarter panels
- Rear window
- Decklid (the horizontal surface between rear window and trunk on sedans)
These components define the vehicle’s rear styling while providing access to cargo areas.
What is the difference between a trunk and a hatchback?
Trunk (or boot):
- Separate compartment behind the rear seats
- Typically has a horizontal opening lid
- Cargo area is isolated from the passenger cabin
- Common in sedans and coupes
Hatchback:
- Cargo area is integrated with the passenger cabin
- Features a large, angled door that includes the rear window
- Provides greater cargo flexibility with folding seats
- Offers increased access through the larger opening
This fundamental design difference affects both the vehicle’s appearance and practical utility.
What Is The Main Part Of A Car?
The body shell or unibody structure forms the main part of a modern car. This integrated framework includes:
- Floor pan
- Firewall
- A, B, and C pillars
- Roof structure
- Front and rear rails
- Side sills
This central structure provides mounting points for all other systems and creates the passenger safety cell.
What is the front body of a car called?
The front body section is often called the “front end” or “front clip” and includes:
- Hood/bonnet
- Front fenders
- Front bumper assembly
- Grille
- Headlights
- Radiator support panel
These front part of a car components create the vehicle’s distinctive face while housing critical cooling and lighting systems.
What are the major automotive components in a car?
Major automotive body components include:
- Body structure (unibody or body-on-frame)
- Closure panels (doors, hood, trunk/hatch)
- Exterior panels (fenders, quarter panels)
- Bumper systems
- Glass (windshield, windows)
- Lighting systems
- Interior trim and structure
These form the visible and structural elements of the vehicle, distinct from powertrain and chassis systems.
What is the name of the body part that holds the car doors?
The body part that secures the doors is the door pillar, specifically:
- A-pillar: Where front doors attach
- B-pillar: Where rear doors attach in 4-door vehicles
The door hinges mount to these reinforced structural pillars, which are critical elements in the vehicle’s side-impact protection system. Modern vehicles engineer these pillars for optimal strength while minimizing visual obstruction.

